Accurate indoor tracking — at the scale of centimetres — is the new gold standard for asset monitoring, robotics, and smart spaces. GPS is fundamentally limited indoors, but Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology, paired with ESP32 microcontrollers, delivers the precision necessary for modern digital applications. This project demonstrates a complete, scalable UWB indoor positioning system built with Qorvo DWM3000 modules and ESP32 MCUs, leveraging robust two-way ranging and real-time location visualisation.
Why Choose UWB over Traditional Indoor Positioning?
Traditional approaches such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer only meter-level accuracy and are susceptible to signal reflection issues. UWB, by contrast, uses nanosecond-pulse radio and precise time-of-flight measurement between anchors and tags, achieving 10cm accuracy even in cluttered environments. This enables asset tracking, navigation, and automation in warehouses, hospitals, factories, and AR/VR applications where traditional systems fail.
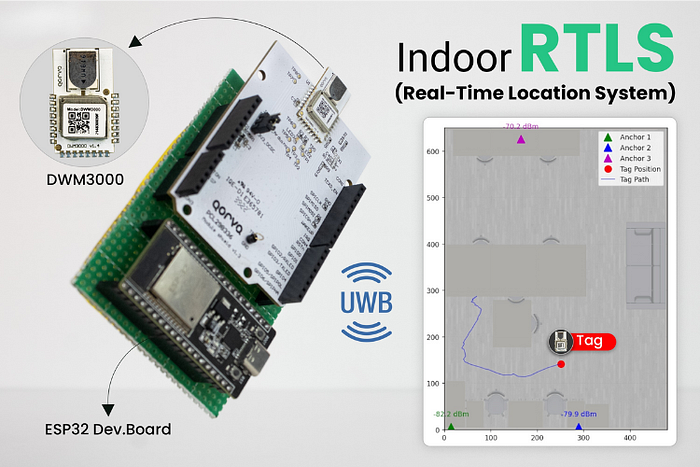
Project Overview and Architecture
Core Hardware:
- ESP32-WROOM microcontroller for wireless networking and onboard processing.
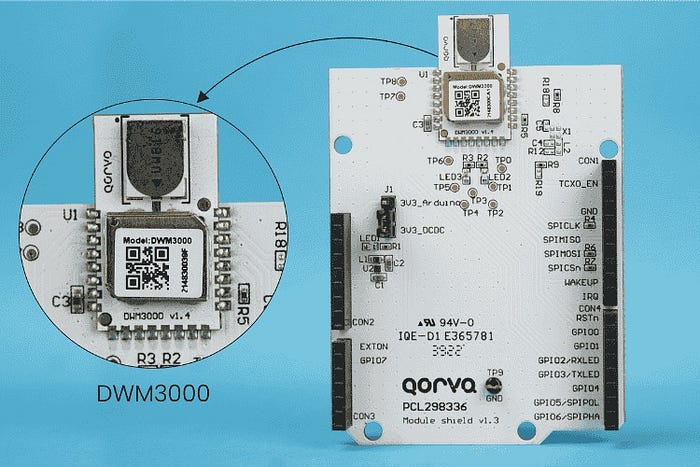
- Qorvo DWM3000 UWB module — fully integrated, supports IEEE 802.15.4z, and includes antennas for global operation.
- Minimum three anchors, fixed at known locations, with the tag device moving in the environment.
- Wi-Fi connectivity for real-time data streaming to a Python-based visualisation host.
Accuracy:
- Sub-10cm, based on calibrations of antenna delay and least-squares trilateration algorithms.
- Robust against multipath and NLOS (Non-Line-of-Sight) thanks to UWB physics and advanced filtering.
Implementation Steps
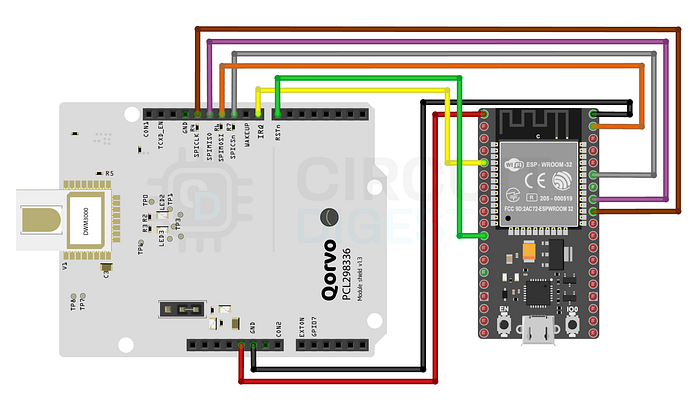
1. Hardware Connections
- Connect Qorvo DWM3000 modules via SPI with the ESP32 boards.
- Establish anchor positions in the environment, ensuring line-of-sight if possible for maximum accuracy.
- Connect ESP32 tags to power and local Wi-Fi.
2. Firmware Setup
- ESP32 tag firmware manages ranging with each anchor and sends JSON-formatted data over TCP to the host computer.
- Anchor firmware handles incoming requests and performs timing protocols for double-sided two-way ranging.
- Driver class for DWM3000 abstracts low-level SPI, register access, RF configuration, and analytics.

3. Real-Time Trilateration and Visualisation
- Python script running on the host listens for incoming data, parses anchor distances, and applies least-squares trilateration.
- Matplotlib visualises real-time position on a floorplan, plots tag movement as a trace, and displays live signal strengths for all anchors.
- Optional enhancements include additional anchors for 3D tracking, web-based dashboards, and multiple tag support.
Key Project Features
High Accuracy:
- UWB positioning precision reaches 10cm or better after calibration.
- Ranging resilient against signal multipath and NLOS effects.
Scalability & Flexibility:
- Easy expansion with extra anchors, support for multi-tag deployments.
- Modular firmware allows quick adaptation to tag, anchor, or network changes.
Security:
- IEEE 802.15.4z-compliant DWM3000 module supports anti-spoofing and data integrity features for secure asset tracking.
Common Applications
- Smart warehouse automation and AGV navigation
- Healthcare asset tracking and personnel safety zones
- Factory automation, tool inventory, and process monitoring
- Indoor navigation for airports, shopping malls, or event venues
- AR/VR spatial experiences need real-time object location
Troubleshooting & Optimisation Tips
- Calibrate anchor positions and antenna delay for optimal performance.
- Median filtering eliminates noise from sporadic measurements.
- Monitor live RSSI for anchors and adjust antenna orientation or power as needed.
- Expand with additional anchors or switch data visualisation to a browser dashboard for wider deployment.
Conclusion
This UWB Indoor Positioning System using ESP32 is a scalable solution that brings centimetre-level positional accuracy to environments unreachable by GPS. With state-of-the-art hardware, open-source firmware, and Python visualisation, engineers can deploy robust RTLS for assets, people, or robots — in factories, hospitals, or smart cities. Start building, iterate, and transform your indoor environments with next-gen spatial intelligence.
For source code, full schematic, and visualisation tools, visit the official repositories. Feedback, troubleshooting, and upgrade ideas are welcome in the discussion below!