For the past two years, a wave of "Text-to-SQL GenAI" tools flooded the market. Most of them looked impressive in conference demos and marketing threads, but broke down the moment they touched real schemas, multi-step queries, concurrency, or production authentication. Engineers ended up spending months duct-taping prompts, chains, retries, and schema hacks just to keep systems from hallucinating or overloading databases.
Google's MCP Toolbox for Databases takes a different, more realistic approach. Instead of pretending LLMs magically "understand your data," it provides a reliable control plane for how agents access databases: standardized, authenticated, observable, and safe. The result is that agents can perform SQL operations without you writing custom SQL adapters, safety checked so you don't have to debug mystery DB connection failures at 2 AM every now and then.
Let's discuss the benefits of using Google's MCP Toolbox for Databases in full detail and how to make the best use of it. Stick up until the end for full setup. Non-members can read the full article here.
What the MCP Toolbox Actually Does
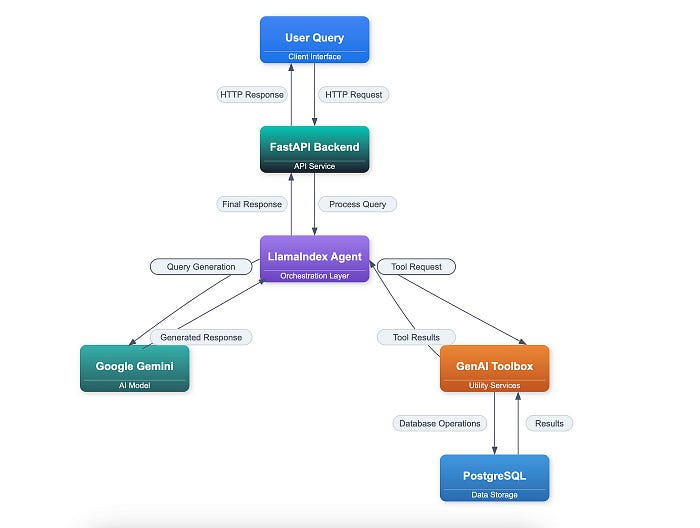
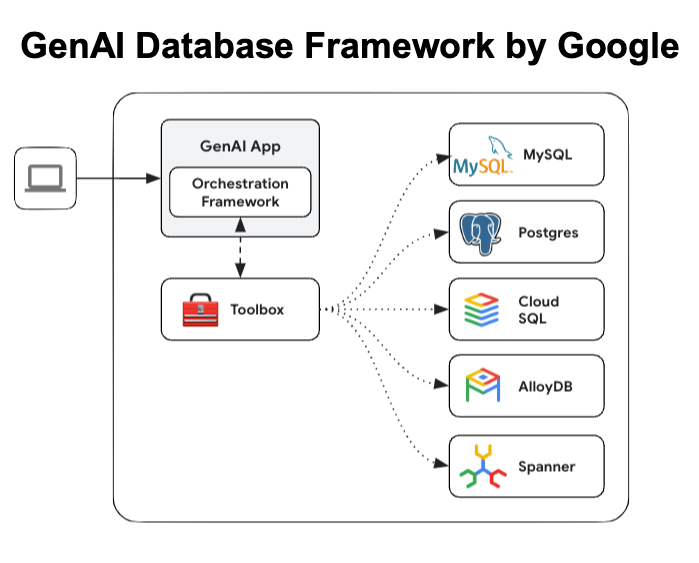
Google's MCP Toolbox for Databases (formerly the "Gen AI Toolbox for Databases") is an open-source server that exposes database operations to AI agents via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It sits between your agent framework (LangChain, LangGraph, LlamaIndex, etc.) and your database, handling:
- Connection pooling
- Authentication and access control
- Schema-aware tool definitions
- Observability via OpenTelemetry
- Hot reloads for rapid iteration
Instead of reinventing safe database access in every agent project, you define tools once in YAML and reuse them anywhere.
Key Benefits for Engineers
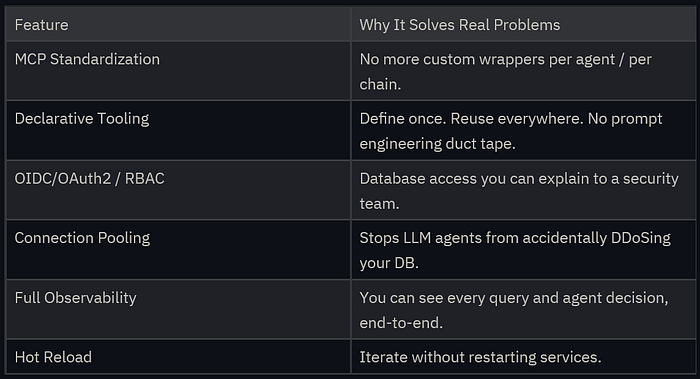
This is the boring, reliable kind of tooling that production systems actually need.
Supported Databases
- PostgreSQL / MySQL (self-managed)
- Cloud SQL / AlloyDB / Spanner (managed)
BigQuery connectors are expected next.
Core Values
At its core, the toolbox enables AI agents to finally perform what was being promised for the last two year at production grade. Tasks like:
- Natural language querying: Translate user questions (e.g., "Show me sales data for Q3") into SQL and execute them securely.
- Database management automation: Generate schema-aware code or automate maintenance tasks.
- Context-aware code generation: Assist in IDEs for writing efficient SQL based on database schemas.
It's particularly powerful for agentic workflows, where AI agents decide which tools to call dynamically, and the toolbox ensures those calls are executed safely and efficiently. The project is hosted on GitHub at googleapis/genai-toolbox, where it's actively maintained by Google Cloud teams, with contributions encouraged from the community.
How It Compares to the "Text-to-SQL Tool" Crowd
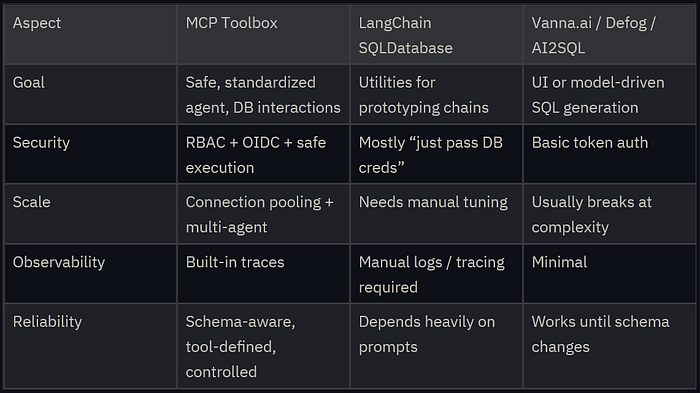
Why Google's Approach is Better and More Reliable Long-Term
1. Production-Ready Infrastructure
Unlike lightweight tools like Vanna.ai or Defog, which shine for quick NL-to-SQL demos but falter in production (e.g., no native handling of concurrent queries or auth failures), the Toolbox embeds best practices like connection pooling and OIDC from day one. This reduces "prompt engineering debt" and operational toil, common pitfalls in direct LLM-to-DB setups where errors cascade silently.
2. Standardization via MCP
MCP is like a "USB-C for AI data access," standardizing how agents interact with tools/databases. This contrasts with fragmented approaches in LangChain (e.g., custom chains per DB) or proprietary tools like AI2SQL, making the Toolbox more interoperable and less vendor-locked. As AI ecosystems mature, MCP adoption (pushed by Google) will ensure longevity, avoiding obsolescence seen in older Text-to-SQL libs.
3. Enterprise Reliability
Backed by Google's Cloud expertise, it integrates seamlessly with Vertex AI (for Gemini models) and services like Cloud SQL, offering SLAs, auto-scaling, and compliance (e.g., SOC 2). Long-term, this means better uptime and evolution, e.g., planned support for multi-DB federation, versus community-driven tools that may lag on security patches. In benchmarks, Gemini-powered setups via the Toolbox outperform generic LLMs on SQL accuracy due to schema grounding and reduced hallucinations.
4. Developer Velocity
Reduces boilerplate by 80–90% compared to raw LangChain SQL chains, per user reports, while enabling agentic flows (e.g., multi-tool orchestration) that simpler Text-to-SQL tools can't match.
In short, if you're prototyping, LangChain or Vanna.ai might suffice. For building reliable, scalable GenAI apps that last (e.g., in finance or healthcare), the Toolbox's focus on secure, observable infrastructure makes it superior.
Setup Guide (10 Minutes)
1. Install
brew install mcp-toolbox2. Define Tools (tools.yaml)
sources:
my-pg-source:
kind: postgres
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 5432
database: toolbox_db
user: toolbox_user
password: ${DB_PASSWORD}
tools:
search-hotels-by-name:
kind: postgres-sql
source: my-pg-source
parameters:
- name: name
type: string
statement: SELECT * FROM hotels WHERE name ILIKE '%' || $1 || '%';
toolsets:
default:
- search-hotels-by-name3. Run
./toolbox --tools-file tools.yaml4. Use from LangChain
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
from toolbox_langchain import ToolboxClient
async with ToolboxClient("http://127.0.0.1:5000") as client:
tools = await client.load_toolset("default")
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-1.5-pro")
agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, tools)
executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools)
print(executor.invoke({"input": "Find hotels named Grand."})["output"])The Toolbox handles the hard parts automatically.
Conclusion: Avoid Reinventing Infrastructure You Don't Want to Maintain
A lot of developers burned time on flashy Text-to-SQL products that were optimized for staged demos, not production. They looked good until they hit:
- multiple schemas
- complex joins
- concurrency
- real permissions
- real reliability expectations
The MCP Toolbox avoids all of those failure modes by focusing on infrastructure first: control planes, authentication, pooling, observability, and standardization.
If you're building actual agent systems, not toy chatbots, this is the right foundation to build on.
Repo: https://github.com/googleapis/genai-toolbox Docs: https://googleapis.github.io/genai-toolbox/getting-started/introduction/
If you've already built a system with the MCP Toolbox and feel like I've missed on something, please let me know in the comments. If you liked this article, please clap and share. Thanks for reading!